Cloud Business Software A Comprehensive Guide
Cloud business software is revolutionizing how companies operate, offering scalable, accessible, and cost-effective solutions. From streamlining workflows to enhancing collaboration, cloud-based applications are transforming industries. This guide delves into the core functionalities, market landscape, benefits, security considerations, and future trends of cloud business software, providing a comprehensive overview for businesses of all sizes.
We’ll explore various categories of cloud software, including Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and project management tools, comparing them to traditional on-premise solutions. We’ll also examine crucial aspects like data security, integration capabilities, and the crucial process of selecting and implementing the right software for your specific needs. Understanding these factors is essential for maximizing the return on investment (ROI) and achieving optimal business outcomes.
Defining Cloud Business Software
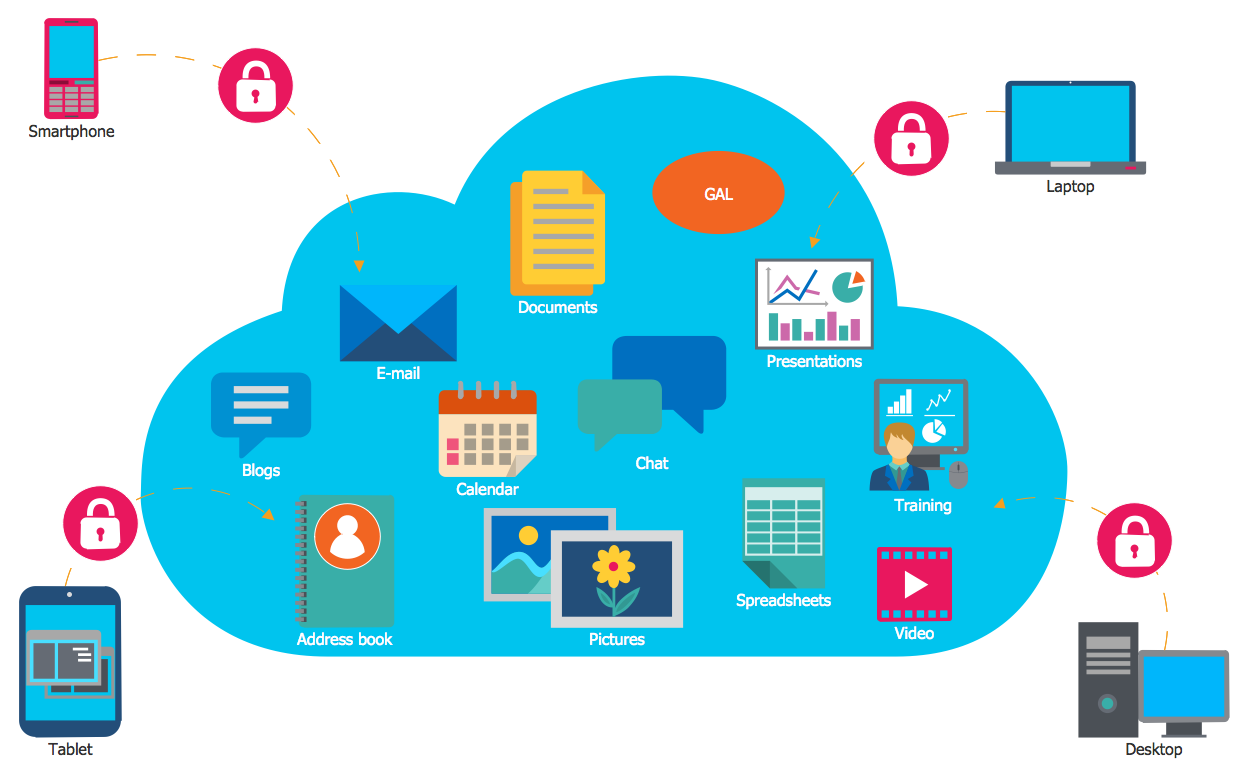
Cloud business software represents a paradigm shift in how organizations manage their operations. Instead of relying on locally installed applications and servers, businesses leverage internet-connected remote servers to access and utilize software applications. This approach offers significant advantages in terms of scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it an increasingly popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
Cloud business software provides a suite of tools designed to streamline various aspects of a company’s operations. These tools often integrate seamlessly, allowing for efficient data sharing and collaboration across departments. Core functionalities typically include data storage and management, user access control, automated workflows, and reporting and analytics capabilities. The level of sophistication and specific features will vary depending on the software and the needs of the business.
Categories of Cloud Business Software
Cloud-based business software solutions are available across a broad spectrum of functionalities, addressing diverse business needs. Understanding these categories helps businesses choose the most suitable options.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM software helps businesses manage interactions with current and potential customers. Features typically include contact management, sales pipeline tracking, marketing automation, and customer service tools. Examples include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): ERP systems integrate various business processes, including planning, purchasing, inventory management, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources. These comprehensive systems provide a centralized view of the entire organization’s operations. Popular examples include SAP S/4HANA, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
- Project Management Software: These tools help teams plan, organize, and track projects, improving collaboration and efficiency. Features include task assignment, progress tracking, Gantt charts, and communication tools. Examples include Asana, Trello, and Monday.com.
- Human Capital Management (HCM): HCM software streamlines HR processes, including payroll, recruitment, performance management, and employee training. Popular examples include Workday, BambooHR, and ADP.
On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Business Software
Choosing between on-premise and cloud-based software involves considering several key factors. On-premise solutions require businesses to purchase, install, and maintain their own hardware and software, whereas cloud-based solutions are hosted by a third-party provider.
| Feature | On-Premise | Cloud-Based |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High initial investment, ongoing maintenance costs | Lower initial cost, subscription-based fees |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, requires significant investment to expand | Highly scalable, easily adjusted to changing needs |
| Accessibility | Access limited to the location of the server | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection |
| Security | Security responsibility rests solely with the business | Security managed by the provider, but business still has responsibilities |
| Maintenance | Requires dedicated IT staff for maintenance and updates | Maintenance and updates handled by the provider |
Market Landscape of Cloud Business Software
The cloud business software market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape, characterized by intense competition, continuous innovation, and significant growth potential. Understanding the major players, current trends, and competitive advantages is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage the power of cloud-based solutions. This section provides an overview of this multifaceted market.
The market is driven by the increasing demand for scalable, flexible, and cost-effective software solutions, particularly amongst small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) who find traditional on-premise software too expensive and complex to manage. The shift towards remote work and the growing adoption of digital transformation strategies further fuel this market expansion.
Major Players in the Cloud Business Software Market
Several prominent companies dominate the cloud business software market, each offering a diverse range of solutions catering to various business needs. These players are often categorized by their specialization, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), or specific industry verticals. Examples of major players include Salesforce (CRM), SAP (ERP), Microsoft (Office 365, Dynamics 365), Oracle (ERP, cloud infrastructure), Adobe (Creative Cloud, marketing software), and Google (G Suite, cloud infrastructure). These companies, along with many others, compete fiercely for market share, constantly innovating and expanding their product portfolios.
Current Market Trends and Future Predictions
Several key trends are shaping the future of the cloud business software market. The increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is enabling the development of more intelligent and automated business processes. For example, AI-powered chatbots are becoming increasingly common in customer service, while ML algorithms are used for predictive analytics and improved decision-making. Another significant trend is the rise of cloud-native applications, specifically designed to leverage the scalability and flexibility of cloud infrastructure. This contrasts with traditional applications that are often adapted from on-premise systems. Furthermore, the increasing demand for integration between different cloud applications is driving the development of robust application programming interfaces (APIs) and integration platforms. Predictions suggest continued strong growth in the cloud business software market, driven by these trends and the ongoing digital transformation initiatives across various industries. Analysts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 15% in the coming years, with specific segments, such as AI-powered solutions, experiencing even faster growth. For instance, the market for AI-powered CRM is projected to experience a CAGR of over 20% due to its ability to enhance customer engagement and personalize interactions.
Competitive Advantages of Cloud Business Software Providers
The competitive landscape is defined by a range of factors. Cost-effectiveness is a major differentiator, with cloud solutions often offering lower upfront costs and predictable monthly expenses compared to traditional on-premise software. Scalability and flexibility are also crucial, allowing businesses to easily adjust their software resources based on their evolving needs. Integration capabilities play a significant role, enabling seamless data exchange between different applications. Finally, the level of customer support and the overall user experience contribute to a provider’s competitive advantage. For example, Salesforce’s success is partly attributed to its robust ecosystem of partners and extensive customer support, while Microsoft leverages its existing user base and wide range of integrated products to maintain its market position. Providers often differentiate themselves by focusing on specific industry verticals or offering specialized features and functionalities.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Cloud Business Software

The decision to adopt cloud-based business software represents a significant strategic move for any organization, regardless of size. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages is crucial for making an informed choice that aligns with business goals and operational realities. This section will explore the key aspects of cost, scalability, security, and accessibility, highlighting the benefits and potential drawbacks of cloud solutions.
Cost-Effectiveness of Cloud Business Software
Cloud-based software often presents a more cost-effective alternative to traditional on-premise solutions. Businesses avoid the substantial upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure. Instead, they typically pay a recurring subscription fee, which can be more predictable and manageable, especially for smaller businesses with limited budgets. Furthermore, cloud providers often handle maintenance, updates, and security patches, reducing the need for dedicated IT staff and associated costs. For example, a small startup could leverage a cloud-based CRM for a fraction of the cost of setting up and maintaining a comparable on-premise system. This allows them to allocate resources to other critical areas of their business.
Scalability and Flexibility of Cloud Solutions
Cloud solutions offer unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Businesses can easily adjust their resource allocation based on fluctuating demands. Need more storage space during peak seasons? Simply upgrade your plan. Experiencing rapid growth and requiring more user licenses? Cloud providers can accommodate this with minimal disruption. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations in demand. Contrast this with the limitations of on-premise systems, where scaling up often requires significant capital investment and time.
Security Considerations in Cloud Business Software
Security is a primary concern when considering cloud-based solutions. While reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure and protocols, data breaches are still possible. Businesses must carefully evaluate the security measures offered by the provider, including data encryption, access controls, and disaster recovery plans. Choosing a provider with robust security certifications and a proven track record is essential. Furthermore, businesses should implement their own security best practices, such as strong password policies and employee training, to minimize risks.
Accessibility and Collaboration Features
Cloud-based software enhances accessibility and collaboration. Employees can access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering remote work and increased productivity. Real-time collaboration tools, such as shared documents and instant messaging, streamline workflows and improve communication. This flexibility is crucial in today’s increasingly mobile and distributed workforce. For example, a geographically dispersed sales team can access customer information and update sales records simultaneously, leading to improved efficiency and responsiveness.
Comparison of Benefits and Drawbacks
| Feature | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront investment, predictable subscription fees, reduced IT overhead | Potential for unexpected costs if usage exceeds limits, vendor lock-in |
| Scalability | Easy to scale resources up or down based on demand, flexible resource allocation | Potential for performance issues during peak usage, reliance on internet connectivity |
| Security | Robust security measures offered by reputable providers, data backups and disaster recovery | Risk of data breaches, reliance on third-party security, potential for data loss |
| Accessibility | Access data and applications from anywhere with internet connection, enhanced collaboration | Dependence on internet connectivity, potential security risks associated with remote access |
Integration and Interoperability
Seamless integration is paramount in the modern business landscape, especially when leveraging multiple cloud-based applications. The ability to effortlessly share data and automate workflows across different platforms significantly boosts efficiency, reduces manual errors, and unlocks a more holistic view of business operations. Without robust integration capabilities, businesses risk data silos, duplicated efforts, and ultimately, a less effective use of their chosen software.
The core benefit of integrated cloud business software lies in its ability to streamline processes and improve data flow. Effective integration eliminates the need for manual data entry between different systems, minimizing the risk of human error and saving valuable time. This automated data exchange fosters better collaboration between departments and provides a single source of truth for critical business information. Furthermore, integrated systems can trigger automated workflows, such as sending notifications upon specific events or automatically updating records across multiple platforms.
Successful Integrations of Cloud-Based Tools
Several successful examples demonstrate the power of integrated cloud business software. For instance, integrating a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system like Salesforce with a marketing automation platform such as HubSpot allows for seamless lead management and targeted marketing campaigns. Data on customer interactions within the CRM automatically updates marketing lists, ensuring campaigns reach the right audience at the right time. Another compelling example is the integration of project management tools like Asana or Monday.com with communication platforms such as Slack. This integration allows for automated updates on project progress, task assignments, and deadlines, keeping team members informed and aligned. Finally, the combination of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software like SAP with financial management tools like NetSuite provides a comprehensive view of financial performance, linking operational data to financial outcomes.
Evaluating Cloud Software Interoperability
Before implementing new cloud business software, a thorough evaluation of its interoperability is crucial. This involves examining the software’s Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and the availability of pre-built connectors or integrations with existing systems. A robust API allows for flexible and custom integration with other platforms. The existence of pre-built connectors simplifies the integration process, reducing development time and cost. Furthermore, it’s important to assess the software vendor’s commitment to ongoing integration support and the availability of documentation and community resources to aid in troubleshooting. A thorough due diligence process involving testing various integration scenarios, including data migration and real-time data synchronization, is also recommended. Understanding the potential limitations and constraints of specific integrations is equally important, allowing for realistic expectations and informed decision-making.
Implementation and Deployment Strategies
Successfully implementing cloud business software requires a well-defined strategy tailored to the organization’s specific needs and existing infrastructure. The choice of approach significantly impacts the project’s timeline, budget, and overall success. Several key factors must be considered, including the organization’s size, technical expertise, existing IT systems, and the complexity of the chosen software.
The implementation process typically involves several phases: planning, design, development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance. Each phase requires careful consideration and execution to minimize disruption and maximize the return on investment. Different approaches exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Deployment Models
Organizations can choose from several deployment models when implementing cloud business software. The optimal model depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the level of control required.
- Public Cloud: This model involves using a third-party provider’s infrastructure and resources. It offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use, but may raise concerns about data security and vendor lock-in. Examples include using AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform to host applications and data.
- Private Cloud: This model uses a dedicated cloud infrastructure managed by the organization itself or a third-party provider. It offers greater control and security but is typically more expensive and requires more technical expertise to manage. A company might choose this to maintain strict compliance requirements.
- Hybrid Cloud: This approach combines public and private cloud resources to leverage the benefits of both. Sensitive data might be stored in a private cloud while less sensitive data and applications are hosted in a public cloud. This provides flexibility and scalability while maintaining control over critical data.
- Multi-Cloud: This involves using multiple public cloud providers simultaneously to enhance resilience, avoid vendor lock-in, and optimize costs. An organization might use AWS for storage, Azure for compute, and Google Cloud for analytics.
Successful and Unsuccessful Implementations
Successful implementations are characterized by thorough planning, realistic expectations, strong stakeholder buy-in, and effective change management. For example, a company successfully migrating its CRM system to a cloud-based platform saw improved customer service response times and increased sales productivity due to streamlined processes and improved data accessibility. Conversely, unsuccessful implementations often result from inadequate planning, lack of user training, insufficient testing, and poor communication. A notable failure involved a large retailer attempting a rapid, poorly-planned migration of their e-commerce platform, leading to significant downtime and reputational damage.
Best Practices for Minimizing Disruption
Minimizing disruption during a cloud migration requires careful planning and execution. Key best practices include:
- Thorough Planning and Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of existing systems, identify potential challenges, and develop a detailed migration plan.
- Phased Rollout: Implement the new system in phases, starting with a pilot program to test and refine the process before a full-scale deployment.
- Robust Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training to users and offer ongoing support to address any issues or questions.
- Effective Communication: Keep stakeholders informed throughout the process and address concerns promptly.
- Data Migration Strategy: Develop a detailed data migration plan to ensure data accuracy and integrity during the transition.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Implement robust disaster recovery and business continuity plans to minimize the impact of unexpected outages.
In conclusion, embracing cloud business software presents significant opportunities for growth and efficiency. By carefully considering the benefits, drawbacks, and security implications, and by selecting a solution that aligns with specific business requirements, organizations can leverage the power of the cloud to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and achieve a competitive edge. The ongoing evolution of cloud technology, particularly with advancements in AI and automation, promises even greater potential for businesses in the years to come. Strategic planning and informed decision-making are key to harnessing the full potential of this transformative technology.
Cloud business software offers significant advantages for modern companies, boosting efficiency and scalability. A key consideration when implementing such software is reliable hosting, and a popular choice is leveraging the robust infrastructure provided by hosting in Google Cloud. This ensures your cloud business software operates smoothly and securely, maximizing its potential for growth and productivity.
Cloud business software offers numerous advantages for modern enterprises, streamlining operations and boosting efficiency. A key component of a robust cloud strategy often involves leveraging reliable hosting solutions, such as those provided by google cloud hosting services , which ensures scalability and security. Ultimately, the right cloud infrastructure significantly impacts the success of your chosen cloud business software.
Posting Komentar untuk "Cloud Business Software A Comprehensive Guide"